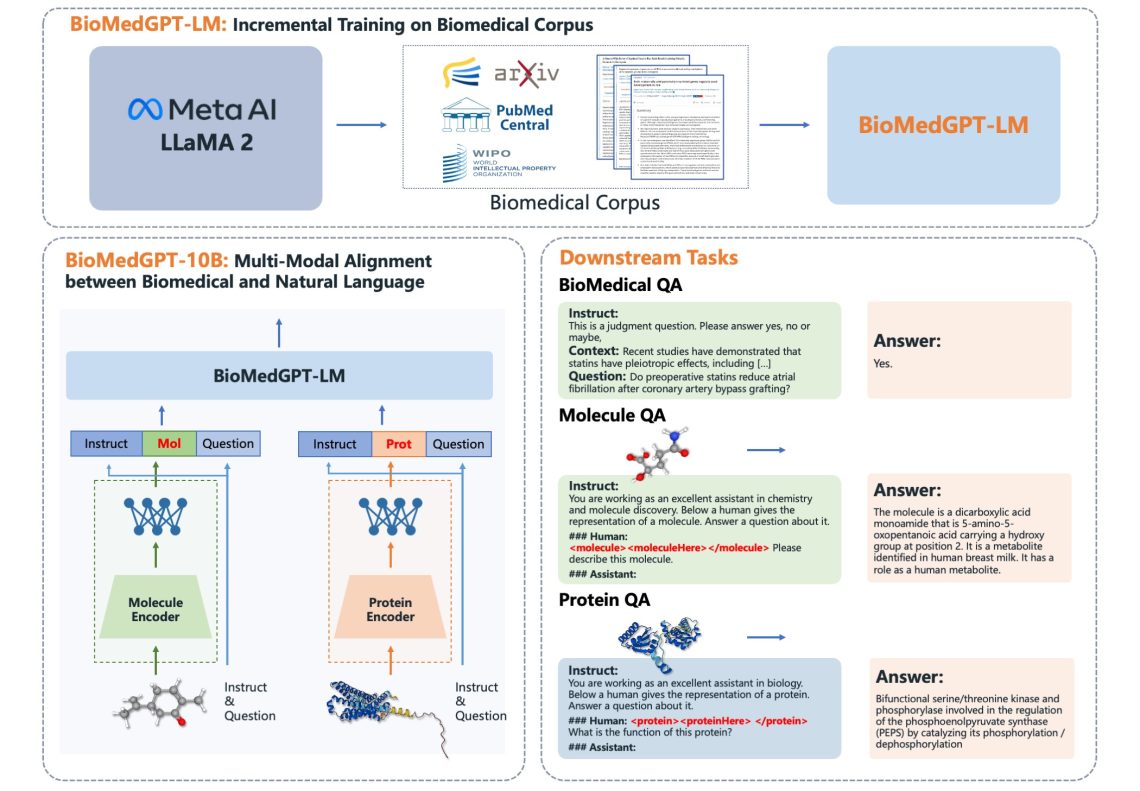
BiomedGPT, a groundbreaking AI model, is redefining how healthcare providers tackle a myriad of medical and scientific tasks. Recently highlighted in Nature Medicine, this open-source AI is designed as a “generalist” capable of excelling in diverse biomedical functions without the need for task-specific training. This development represents a significant leap in AI application within the medical sector, promising to enhance efficiency and accuracy across various domains. BiomedGPT merges two AI capabilities: interpreting biomedical images and analyzing scientific texts. This dual approach equips medical professionals with a robust decision-support tool, capable of handling complex challenges by drawing insights from extensive biomedical imagery databases and research literature. Key to BiomedGPT’s innovation is its foundation model structure. Unlike traditional AI systems tailored for specific roles, BiomedGPT’s versatility allows it to perform multiple tasks effectively using the same core technology. Its training on vast biomedical datasets, including images and text, has yielded 16 state-of-the-art results across 25 datasets and nine tasks, as demonstrated in human evaluations on radiology tasks. In practical terms, BiomedGPT has the potential to streamline numerous healthcare processes. For instance, it can interpret complex medical images, assist researchers by synthesizing scientific literature, and even predict molecular behaviors to aid drug discovery. This capability not only accelerates medical research but also enhances clinical decision-making. However, implementing such technology isn’t without challenges. Clinical validation is paramount to ensure its accuracy and reliability in real-world settings. Massachusetts General Hospital’s collaboration in testing the model with radiologists has been pivotal in refining its clinical applicability, ensuring it meets the rigorous demands of healthcare environments. The development of BiomedGPT has been a collaborative effort involving experts from various institutions, including Lehigh University, University of Georgia, and Stanford University. This interdisciplinary approach was crucial in handling the complex challenges of creating an AI model capable of improving patient care across diverse medical scenarios. As businesses consider adopting AI like BiomedGPT, it’s crucial to address potential implementation challenges, including ensuring data diversity for training and aligning AI capabilities with existing healthcare workflows. The promise of BiomedGPT lies in its ability to provide faster, more accurate, and more efficient healthcare solutions, marking a significant advancement in medical AI applications.
- AI Products
For startups
For Professionals
- AI Services
For corporations
For Goverments
For Professionals
- Consulting
For corporations
For Goverments
For Professionals
- About
- Cases
- AI Products
For startups
For Professionals
- AI Services
For corporations
For Goverments
For Professionals
- Consulting
For corporations
For Goverments
For Professionals
- About
- Cases