Recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are reshaping the business landscape, prompting leaders to reassess their workforce strategies and operational models. A comprehensive review of AI automation prediction methodologies reveals key insights for decision-makers navigating this technological shift.
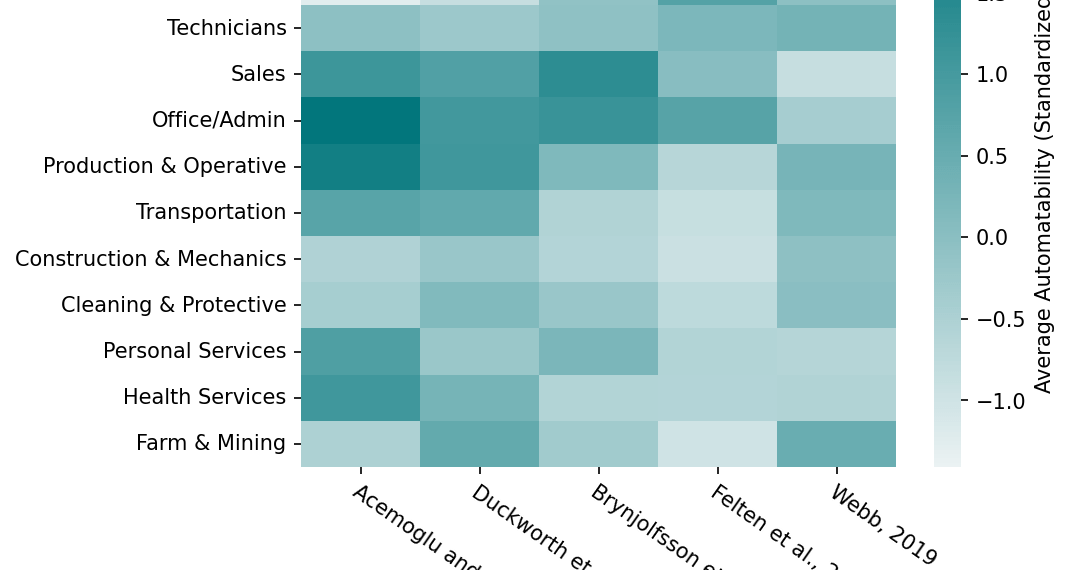
Predicting AI’s Impact: Three Main Approaches
- Task Feature Analysis: Evaluates job tasks based on their susceptibility to automation, often using AI researchers’ opinions on current and near-future AI capabilities.
- Task-Patent Mapping: Correlates job task descriptions with AI-related patents to gauge automation potential.
- Automation Forecasting Surveys: Directly asks AI experts to predict when specific tasks or occupations will become automatable.
Key Findings for Business Leaders:
- High-Skill Jobs at Risk: Unlike traditional automation, AI potentially impacts high-wage, cognitive-intensive roles such as managers and professionals.
- Varied Predictions: Different methodologies yield inconsistent results, highlighting the complexity of forecasting AI’s impact.
- Partial Automation Common: Many tasks are likely to be partially automated, enhancing worker productivity rather than fully replacing human labor.
- Deskilling Effect: AI tools often benefit less experienced workers more, potentially reducing skill gaps within organizations.
Real-World Evidence of AI Impact:
- Customer Support: AI assistants improved agent productivity by 14%, primarily by elevating less experienced workers’ performance.
- Software Engineering: Programmers using AI coding assistants completed tasks 55% faster, with the most significant gains for slower participants.
- Translation Services: Introduction of AI translation led to a 30% decrease in demand for human translators, particularly for routine tasks.
- Management Consulting: AI assistance increased task completion speed by 25% and quality scores by over 40% for product development tasks.
Challenges in Predicting AI Automation:
- Interpretability: Difficulty in translating automation ratings into clear predictions of impact type, extent, and timeline.
- Deployment Realities: Many predictions fail to account for practical implementation challenges, regulatory issues, and economic incentives.
- Rapid AI Progress: Keeping prediction models updated with the latest AI capabilities remains an ongoing challenge.
Implications for Business Leaders:
- Workforce Planning: Prepare for potential shifts in skill requirements across all job levels, including high-skill positions.
- Investment Strategies: Consider AI’s potential to enhance productivity in various roles when allocating resources for technology adoption.
- Training and Development: Focus on upskilling programs that complement AI capabilities, particularly for tasks requiring complex reasoning or creativity.
- Operational Redesign: Explore opportunities to restructure workflows around AI-enhanced tasks for maximum efficiency gains.
- Ethical Considerations: Develop strategies to address potential workforce displacement and ensure equitable distribution of AI’s benefits.
As AI continues to evolve, business leaders must stay informed about its potential impacts and remain adaptable in their strategies. While predicting exact outcomes remains challenging, understanding the broader trends and methodologies can help organizations prepare for and capitalize on the AI-driven transformation of work.